Notice that the efficiencyvariance is not applicable to the fixed overhead varianceanalysis. This could be for many reasons, and the production supervisor would need to determine where the variable cost difference is occurring to better understand the variable overhead efficiency reduction. Estimate the total number of standard direct labor hours that are needed to manufacture your products during 2023.
Which activity is most important to you during retirement?
- The standard overhead rate is calculated by dividing budgeted overhead at a given level of production (known as normal capacity) by the level of activity required for that particular level of production.
- The standard overhead rate is the total budgeted overhead of $10,000 divided by the level of activity (direct labor hours) of 2,000 hours.
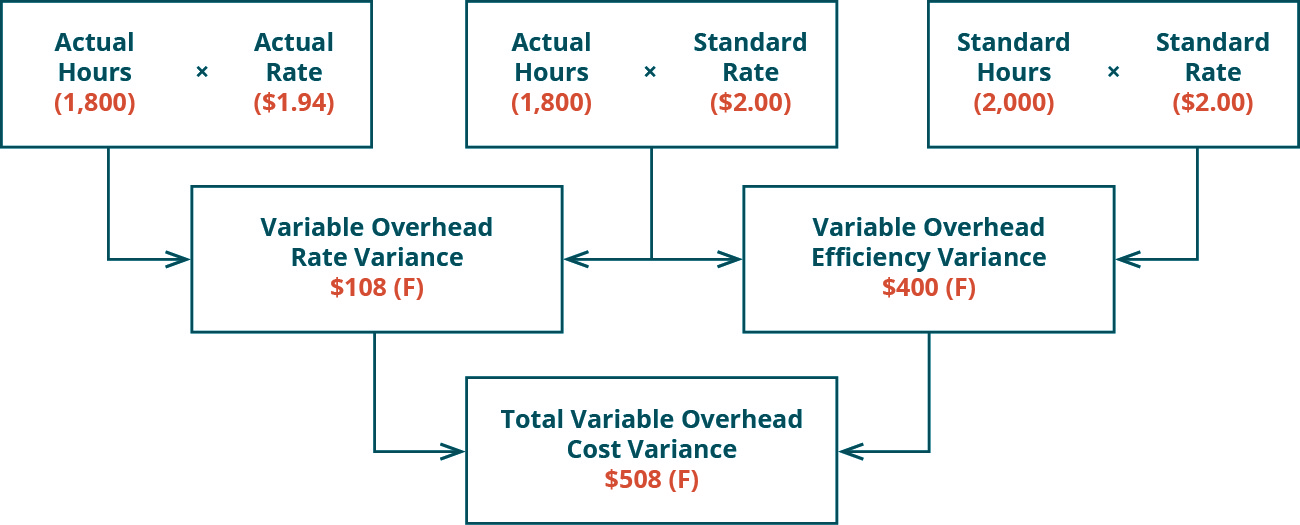
- By showing the total variable overhead cost variance as the sum of the two components, management can better analyze the two variances and enhance decision-making.
- In our example, we budgeted the annual fixed manufacturing overhead at $8,400 (monthly rents of $700 x 12 months).
- This example provides an opportunity to practice calculating the overhead variances that have been analyzed up to this point.
- Fixed overhead budget variance is favorable when actual fixed overhead incurred are less than the budgeted amount and it is unfavorable when the actual fixed overheads exceed the budgeted amount.
Instead, Jerry’s mustreview the detail of actual and budgeted costs to determine why thefavorable variance occurred. For example, factory rent, supervisorsalaries, or factory insurance may have been lower thananticipated. Further investigation of detailed costs is necessaryto determine the exact cause of the fixed overhead spendingvariance. It is important to start by noting that fixed overhead in themaster budget is the same as fixed overhead in the flexible budgetbecause, by definition, fixed costs do not change with changes inunits produced. Thus budgeted fixed overhead costs of $140,280shown in Figure 10.12 will remain the same even though Jerry’sactually produced 210,000 units instead of the master budgetexpectation of 200,400 units.
What is Variance Analysis? Definition, Explanation, 4 Types of Variances
In this example, the fixed overhead budget variance is positive (2,000 favorable), and the fixed overhead volume variance is negative (-1,040 unfavorable), resulting in an overall positive overhead variance (960 favorable). Fixed overhead budget variance is favorable when actual fixed overhead incurred are less than the budgeted amount and it is unfavorable when the actual fixed overheads exceed the budgeted amount. Variable overhead spending variance is favorable if the actual costs of indirect materials — for example, paint and consumables such as oil and grease—are lower than the standard or budgeted variable overheads.
Related AccountingTools Course
The standard variable overhead rate is typically expressed in terms of the number of machine hours or labor hours depending on whether the production process is predominantly carried out manually or by automation. A company may even use both machine and labor hours as a basis for the standard (budgeted) rate if the use both manual and automated processes in their operations. Since the fixed manufacturing overhead costs should remain the same within reasonable ranges of activity, the amount of the fixed overhead budget variance should be relatively small. Companies typically establish a standard fixed manufacturing overhead rate prior to the start of the year and then use that rate for the entire year.
Fixed overhead costs are the indirect manufacturing costs that are not expected to change when the volume of activity changes. Some examples of fixed manufacturing overhead include the depreciation, property tax and insurance of the factory buildings and equipment, and the salaries of the manufacturing supervisors and managers. An overhead cost variance is the difference between how much overhead was applied to the production process and how much actual overhead costs were incurred during the period.
Clearing the Fixed Overhead Variance Accounts
Let’s say you expected to pay $20,000 in fixed overhead, then if you actually paid $22,000,you would have an unfavorable spending variance of $2,000. This could be for many reasons, and the production supervisor would need to determine where the variable cost difference is occurring to better understand the variable overhead reduction. Looking at Connie’s Candies, the following table shows the variable overhead rate at each of the production capacity levels.
Finance Strategists has an advertising relationship with some of the companies included on this website. We may earn a commission when you click on a link or make a purchase through the links on our site.
The amount of the property tax bill did not depend on the number of units produced or the number of machine hours that the plant operated. Although the fixed manufacturing overhead costs present themselves as large monthly or annual expenses, they are part of each product’s cost. Because fixed overhead costs are not typically driven byactivity, Jerry’s cannot attribute any part of this variance to theefficient (or inefficient) use of labor.
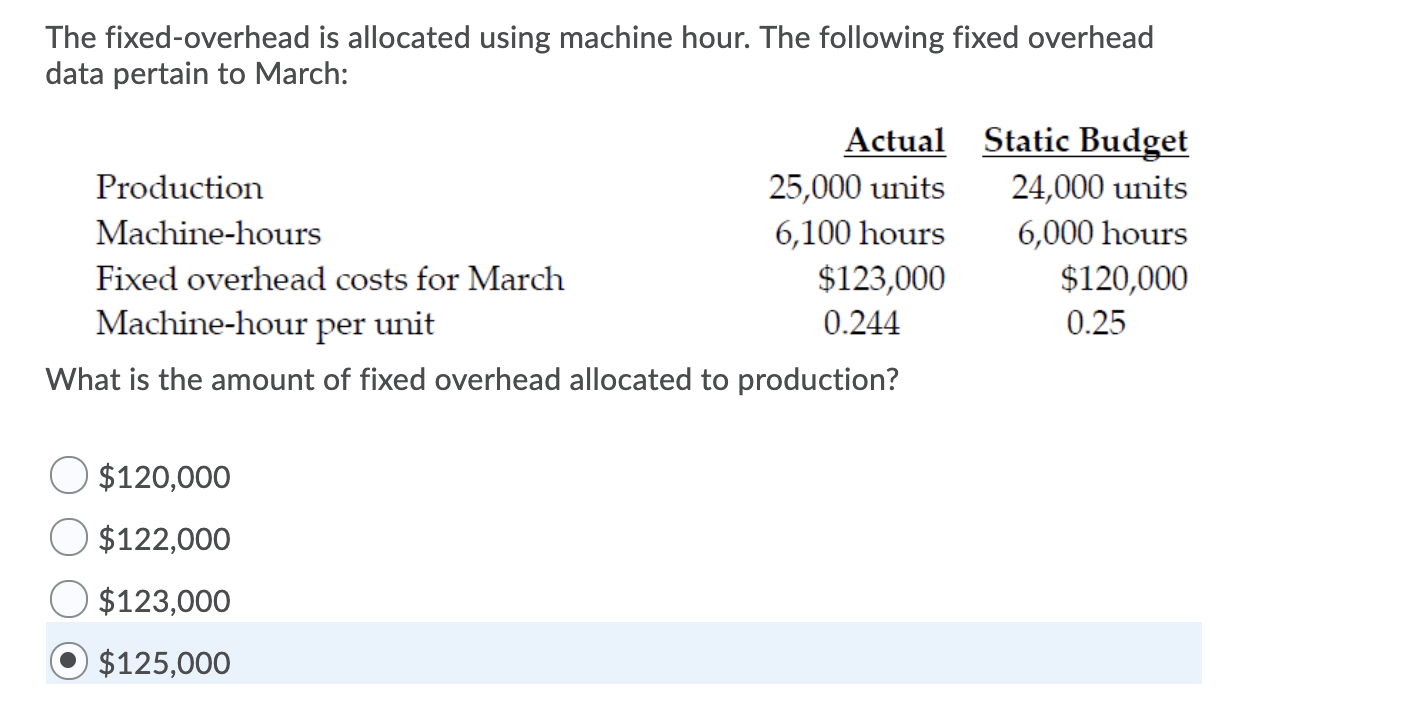
Overhead variances arise when the actual overhead costs incurred differ from the expected amounts. Managers want to understand the reasons for these differences, and so should consider computing one or more of the overhead variances described below. It is not necessary to calculate these variances when a manager cannot how to pay taxes as a freelancer influence their outcome. The fixed manufacturing overhead volume variance is the difference between the amount of fixed manufacturing overhead budgeted to the amount that was applied to (or absorbed by) the good output. If the amount applied is less than the amount budgeted, there is an unfavorable volume variance.